Best Fit and Practices for Owning a 3D Printer and How Can You Run a 3D Print from Start to Finish
The most important piece of this technology is how it can help to resolve the headaches within the manufacturing sector. This additive technology will resolve problems like: “Will the project be done on time?”, “Will the project be done within cost”? and “The job shop we send our work out to has our job delayed.”
What is Additive Manufacturing? It’s the process of taking a CAD design and utilizing 3D printing hardware to build a part with plastic or metal material in a layer by layer process, thus “additive manufacturing.”
What is 3D Printing? 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates a physical object from a digital design. (source: 3D Hubs). It’s adding material to create a part, whereas CNC manufacturing is subtractive manufacturing or “taking material away”.
How does 3D Printing work? It’s a process for making a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model, typically by laying down many successive thin layers of a material. FFF works on an “additive” principle by laying down material in layers; a plastic filament is unwound from a coil of material heated in an extruder head and follows a slice path layer by layer to create a part.
Why 3D Printing? Additive isn’t just a technology for prototyping anymore. The cost of machines are very affordable and the durability/reputability of the materials available are lending to everything from the production of end-use parts and manufacturing aids.
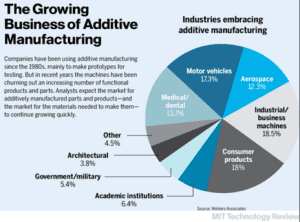
Where does 3D Printing technology fit in manufacturing? The production of parts that are low in volume and complex in geometry. When it comes to creating things like manufacturing tools specific to an application, like jigs, fixtures, and check gauges additive makes a lot of sense. Parts for example that need to be held for a CMM machine may need fixturing that is specific to that one part, and a CMM may have to hundreds of parts over the span of a year that are all different, with an in-house 3D printer all those points on a part can have specific fixturing that is made quickly and in a cost-effective manner.
